To study the biology or Life science one should be with the question: what is life? although biologist have a vast knowledge of living things, they find much difficulty in defining life which compressor complex physical – chemical system. life is not a definition entity or property. if you look up life in a dictionary, you will find definition such as “the quality that distinguishes vital and functioning Bing from a dead body” but you want find out what that “quality” is.
Life is the property that distinguishes leaving thing from non – living objects. it is not possible to draw a fine line of demarcation between living and nonliving things. for example, virus is a lifeless practical until it becomes active inside a living cell. almost all living organisms share certain basic characteristic which include reproduce and growth, metabolism, movement, responsiveness and adaptation. but not every organism this place all these features and even inorganic substances may exhibit some of them. living things are not only greatly dependent on there physical surrounding they are also inter dependent on other life forms. all living things share some unified and basic characteristics not shared by nonliving objects.
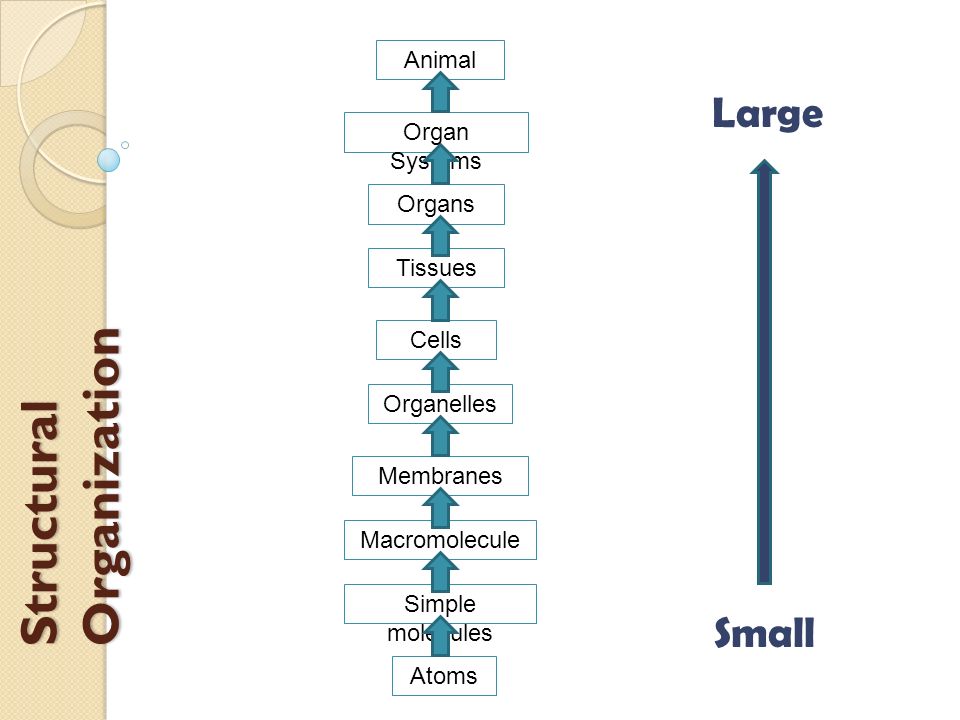
Characteristics of living things

1. Living things are highly organized
Living organisms are made of chemicals and have a highly organized and complex structure based on organic molecules. the structural and functional unit of living organisms is a cell. Some unicellular organisms are free living and processes structures called organelles, that permit them to be self sufficient. more complex organism are multicellular. in the case of higher organisms, cells are organized into tissue. this have a common function like a muscles. tissue are organized into organs. like the kidney. organ are further organized into organ system, like the urinary system. organ system functioning together makeup or living organism. a population is an organization of more than one individual. this is generally and assemblage one species in a particular area at a given time. enlarging our views, next comes a community. a community is composed of many species including plant and animals. an ecosystem not only consider the living things in an area, but also the abiotic environment and the interrelated flow of energy. most complex of all is the biosphere which includes the all the areas of our planet where living things are found.
2. All living things have an ability to grow
Living things grow in size and increase in number. most animals grow until they reach maturity and them remain at a constant size while plants usually continue to increase in size throughout their lifespan. growth is permanent increases in measurable feature such as volume, mass, length, width, etc. cells increases in number by dividing in a process turned mitosis. as the soft tissue increases, so there will be associated increases in size of skeletal support tissue such as bone, shall and wood. when maturity is riched in animals, cell division continuous only at a level to maintain consistent size and to repair loss through damage.
3. All living things have an ability to acquired material and energy
We are capable to convert our food, a form of energy, to chemicals which our body cells can use to thought metabolism. living organisms acquired materials and energy from there environment for metabolism. anabolism is a process that involves synthesis or putting together complex substances from simpler substances and these request energy. catabolism is the final breakdown of complex substances into simpler once and these releases energy. metabolism is the sum total of all biochemical reactions in the body are the balance between anabolism and catabolism.
Some organisms like plant, algae, and some microorganisms are autotrophs. the autotroph we are most familiar with are the green plants that use photosynthesis to make their own “food”. some bacteria depend on cameo synthesis for their energy source. animals and fungi are heterotrophs and capture their food in variety of waves. the ability to acquired and use energy is extremely important for living organisms.
Living organisms actively maintain their complex structure and their constant internal environment a process called homeostasis. in order to survive, organism must be capable to homeostasis. each type of organism has a specialized a way to stay in balance with its external and internal environment. a paramecium process contractile vacuous that pump excess water out of it sale in order to survive in a freshwater environment. you and I have an internal “thermostat” in our brain that hells us maintain a body temperature of about 98.6 degree Fahrenheit.
4. Living things have ability to respire
Living things respire respiration is a complex sequence of chemical reactions which result in the release of energy from food. there are two types of respiratory processes.
Aerobic respiration : carried out by the vast majority of organisms which involve oxygen. the by products of this process are H2O and CO2 both of which are eliminated as waste products. oxygen is obtained from the year or water using organs designed to optimize gaseous exchange. these include the stomata in plants, spiracles in arthropods, Giles in fish, and lungs in mammals. the up takes of Oxygen and simultaneous elimination of carbon dioxide and water is commonly referred to as breathing.
Anaerobic respiration : when oxygen levels, are at a low level it is possible for some simpler organisms and part of more complex 1 to release energy from food in the absence of oxygen. this is a far lace efficient process but a necessary alternative in some cases. the by products of anaerobic respiration are different from aerobic. in humans, oxygen starved muscle cells will respire anaerobically under stress such as heavy physical activity. the by products of this is the lactic acid. East sale respire anaerobically in sugar solution producing ethyl alcohol as the byproduct.
5. Living things have ability to move
Living thing move in a directed and controlled way, moving of their own Accord. non living things only move if they are pushed or pulled by something else. The majority of animals usually move their whole bodies often supported by specialized organ such as fins, wings and legs. these are called locomotory organs moving the animal from place. to place plant movement is not locomotory and does not generally involved moving the whole body.
6. All living things have an ability to respond to their environment
Living organisms are aware of their surrounding and respond to stimuli from there environment. days of 10 result in moment of the individual towards safety. this helps to ensure survival of the organism. for example, as young children we learn to avoid hot stoves and busy streets. plant also have some limited ability to move. they grow up towards the sun, and some have leaves able to turn to follow the sun allowing them to photosynthesize better. there roots grow down to search for water and minerals. if the plant does not get enough sunlight water or minerals it will die.
7. All living things have an ability to adapt
Living organisms adapt to the environmental changes and have the capacity to involve into new types of organisms. modifications enable and organism to survive in its environment. natural selection allow individuals with better adaptations to server better and reproduce more. does there characteristics are passed into future generations and that makes the spaces stronger.
8. All living things have an ability to reproduce
Reproduction is the characteristics of living beings that permits the individuals to make replicas of their kind. living organisms reproduce themselves using a molecular blueprint called DNA. all thought some organic molecules are able to make replication from themselves they lack of the other characteristics of living being. living thing are able to reproduce themselves. if organisms fail to do this population will diminish and disappear as their members die from old age, disease, accident, predication, etc.
There are two fundamental types of reproduction
Asexual reproduction : it involve no exchange of genetic material but it is simple replication to produce a new organism. organisms produced in this way display little or no genetic variation from the parent organism and are called clones. plant growing from tubers or bugs such as potatoes and daffodils are displaying a sexual reproduction.
Sexual reproduction : it involved the combination of genetic material from two parents organism. the offspring from sexual reproduction will generally displace sum of the characteristics of both parent. sexual reproduction in sir that there is high degree of variation within populations. the parent organisms give rise to reproductive cell called gametes. this are formed by a special types of cells division called meiosis. the cell produced in this way has half the normal amount of genetic material. when the gametes from one parent fuse with the gametes of the other the resulting single cell called a zygote has a full complement of genetic material half coming from one parent and have coming from the other.
Matter and energy
Technical speaking matter and energy are interchangeable as expressed by Albert Einstein famous equation e = MC square energy equal matter time the speed of light c square for the chemical reaction that occurs within living organisms however we can treat matter and energy as quite distinct from one other another matter is the physical material of the universe energy is the capacity to do work.
Close and open system
A system is a portion of the in your that is selected within a definite boundary the part of other than the system is called surrounding a system is said to be closed if it can exchange energy but not matter coffee in a stainless steel flas in this energy can be gained or lost but not matter.
A system is said to be open if it can exchange matter and energy with surrounding all living systems are open systems because they are continuously exchanging matter and energy with their surrounding (a system is said to be isolated if it cannot exchange matter and energy with the surrounding coffee in a thermoplastic it can neither gain or loss matter not eat can gain or lost energy.)
Kinetic and potential energy
Energy can exist in several form and maybe converted from one from to another the two major categories of energy are kinetic energy and potential energy kinetic energy is the energy of motion this include not only movement of large objects but also movements such as electrical energy movement of electrons and heat moment of atoms and molecules potential energy is told energy that result from the position or structure of an object and it can be released as kinetic energy under right condition the food which you eat has chemical potential energy some of which is converted into kinetic energy.
Laws of thermodynamics
The laws of thermodynamics describe the basic properties of energy all interactions among pieces of matter are governed by the two laws of thermodynamics this law deals with isolated systems which are any part of the universe that cannot extend their matter and energy with any other parts.
First law of thermodynamics
The first law of thermodynamics states that energy can neither be created nor be destroyed. But energy can change from one from one to another in other words within an isolated system the total quantity of energy remains constant the first law is therefore often called the law of conservation of energy .
second law of thermodynamics
The second law of thermodynamics States that the amount of useful energy always decreases when energy is converted from one from to another in other words every transfer or transformation of energy makes universe disorders no physical process or chemical reaction is 100 per sent efficient entropy is a major of the disorder or randomness within a system.
Exerginic and endergonic reaction.
Chemical reactions fall into two categories: exeegonic and endergonic reactions in exergonic reactions the product molecules have less energy than the reactant molecules so the reaction releases energy . In endergonic reactions the products have more energy than the tag tents so the reaction required and input of energy is organic reactions can occur spontaneously but all reactions including exergonic once required initial input of energy called activation energy to overcome electrical repulsion between reactant molecules exergonic and endergonic reactions maybe coupled together so that the energy liberated by an exergonic reaction drives the endergonic reactions living organism couple exergonic reaction such as energy capture or sugar metabolism with endergonic reactions such as the synthesis of organic molecules.

Both exergonic and endergonic reactions are reversible and can process in either direction due suitable inputs of products reactants and energy all reactions if left to themselves eventually reach a steady state called a chemical equilibrium living organisms provide the necessary inputs in controlled ways that drive reversible reactions in the directions necessary to maintain life.
Metabolism
All living organism required a continuous input of energy and materials the exchange of energy and materials between an organism and its surrounding and conversion of matter and energy within a living organism is term as metabolism all biochemical reactions that occur in an organism is known as metabolism it has two phases namely anabolism and catabolism anabolism reactions consists of series of synthetic reactions which usually required energy anabolism is usually and uphill process anabolism reactions often involve condensation include growth repair storage and reproduction catabolism reactions involve the breakdown of molecule within cells and usually release energy digestion and respiration are catabolic processes breaking of covalent bond religious the energy.
Biochemical pathway
Usually a number of enzymes are untilised in sequence to convert one substance into one or several products via s series of intermediate compounds the chain of reactions is termed as a biochemical or metabolic pathway meany such pathways are going on at the same time in the cell the reactions proceed in a tightly regulated manner to prevent unnecessary West of energy and raw materials metabolic pathways are directed by enzymes which server to control the chemical reactions that occur within cells.
Enzymes : biological catalysts
Enzymes are biological catalysts because they are used to catalysts a West number of chemical reactions for living organism enzymes are vitally important because in there absence biochemical reactions in the cells would be to slow to sustain life the chemical which and enzymes works on turned its substrate the site where the substrate binds in the enzymes is known as active site and exam combines with its substrate to form and enzyme substrate complex after reaction the complex brakes up into products and enzyme a common way of regulating biochemical pathways in cells in by means of alosteric enzymes which process and illus tic site away from the active site when the end product of a metabolic pathway beings to accumulate it may act as anostatic inhibitor for the action of the first enzyme of that pathway this method of regulating mechanism is called end product inhibition and is an example of a negative feedback mechanism.
Homeostasis
Homeostasis is the body’s automatic tendency to maintain a constant internal environment or steady state of the French physiologist Claude Bernard (1857) was first to realize the importance of stability in the internal environment the term homeostasis was coined by the American physiologist Walter Bradford Canon in 1929. Homeostasis is a fundamental property of life to survive energy organism must maintain homeostasis.
Thermoregulation
Many animals have elaborate homeostatic mechanisms for regulating body temperature thermoregulation is the ability to maintain body temperature within certain limits even when the temperature of the environment is very different animals can be divided into two groups poikilothermos and homeothermous.
Poikilothermic means having a variable temperature poikilothermic animals are describe as cold blooded their body temperature changing with fluctuation in the environment temperature if environment is called so is there blood.
Homeothermic means having the same temperature homeothermic animals are popularly described as warm blooded their body temperature is independent of environmental temperature in cold conditions Their body is at a temperature higher than that of their surroundings.
More useful terms are ectothermic and endothermic.ectothermic animals as the word implies gain hit from the environment that is from the Sun and advantage of ectothermic is the absence of direct metabolic cost endothermic animals generate heat from within the body and conserve it there.
Growth
Growth is a vital characteristics of living organisms all organisms grow developed and reproduce growth result in an increase in size weight and synthesis of new protoplasm it takes place by addition of new substances both protoplasmic and apoplasmic eat up to when anabolism is higher than catabolism if energy is obtained at the expense of protoplasmic proteins it result in degrowth which takes place when catabolism is higher than anabolism the process in which reserve food materials is utilized and exhibited negative growth is called degrowth.
During development most organisms inhibit varied rates of growth for different parts of the body known as allmatric growth. The size of the head in human newborns is larger in proportion to rest of the body.
Development
In general growth involves three processes are strategies namely cell proliferation cell enlargement and secretion of large amount of extracellular matrix growth is an important part of development continuing throughout life early embryonic developmental stages constitute antional state of life the biological process of growth and differentiation enable the animal to enter the functional state of life.
Morphogenesis refers to generation of form and structure during development of an individual organism it produces new form by involving cell moments morphogenic movements of large number of sales during development is particularly noticed during gastrulation differentiation results in creasing diversity of cells.
Reproduction
Reproduction is one of the most important life functions it is the only way that living things can perpetuate themselves there are a number of different ways that various kinds of organisms reproduce and compensate for the loss of life due to death.
In simple organism such as amoebas reproduction maybe a sexual that is without the fusion of egg and sperm to form a fertilized egg the only way that variation occurs among a sexually reproducing organism is by genetic mutation a permanent changes in the genes. In most plant and animals sexual reproduction is carried out by the production of gamuts that fused to form fertilized egg the new organism develops from the fertilized egg offspring produced by sexual reproduction are product of the interaction of various genes contributed by the mother and the father such genetic variation provides raw material for the vital processes of evolution and adaptation.
Adaptation
The word adaptation refers to any character sticks of an organism which makes the organism better suited to eats environment it is a characteristics that enhances the survival or reproduction of organisms that beer it adaptation improves adaptations are remarkable the result from natural selection individuals with favorable characteristics replace those with less favorable characteristics this process improves the match between organisms and their environment.
Death
Death results in the loss of life the organisms reproduce to compensate the loss of life death helps in the recycling of elements between living and non living matter such as a recycling his two maintain the balance of matter in nature euthinesis refers to the act of practice of putting painlessly to death specially in case of a person who is suffering from incurable disease.